Computer numerical control (CNC) machining is a specialized manufacturing process that uses computer technology to guide equipment. This makes it possible to automate production processes and increase the volume of production in industrial facilities. Read More…
At GrovTec Machining, we pride ourselves on being the go-to destination for precision turned components and screw machine products. When it comes to fulfilling your machining needs, you need not look any further than our state-of-the-art screw machine shop. Our dedicated team of experienced machinists and cutting-edge equipment allow us to tackle projects of all sizes and complexities.
Our advanced CNC machining centers are equipped with the latest technology, enabling us to produce intricate and accurate parts with tight tolerances. Our team of skilled programmers and machinists can efficiently handle both small and large production runs, delivering exceptional results every time. Whether it's prototyping or full-scale production, we are committed to meeting your CNC machining ...

With nearly 40 years industry experience, we have what it takes to satisfy your every need. We are committed to our CNC machining quality, as our ISO 9001:2008 certification shows.

H & R is a custom manufacturer of high volume superior parts, providing CNC machining for tight tolerance and also lower volume applications too.

Thuro Metal Products is a CNC machining service provider. Our expertise is in the utilization of CNC controlled turning and milling machines as well as multi-spindle, single spindle, and Swiss screw machines.

More CNC Machining Companies
CNC Machining Benefits
CNC machining, or Computer Numerical Control machining, is a manufacturing process that employs computer-controlled machines to create precise and complex parts from various materials. It uses specialized software programmed with G-code, enabling precise control over parameters like speed, location, coordination, and feed rate. This advanced technology provides significant advantages over traditional manual machining methods. The following are a few benefits of CNC machining processes.
Precision and Accuracy:: CNC machining excels in delivering unparalleled precision and accuracy through its computer-controlled automation, consistently producing repeatable results. These machines maintain extremely tight tolerances, often within fractions of a millimeter, reducing human error and ensuring precise dimensions and geometries. The integration of advanced positioning systems, multi-axis capabilities, and digital control with feedback mechanisms enhances the precision of CNC machining. Rigorous quality assurance practices, including in-process inspections and post-machining measurements, further confirm the accuracy of the components. The exceptional precision and accuracy of CNC machining make it essential in industries that demand reliability, functionality, and intricate designs, such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical sectors.
Increased Efficiency:: CNC machining enhances modern manufacturing by automating processes, allowing machines to operate continuously without constant manual oversight, leading to uninterrupted production and optimal machine use. This automation speeds up production cycles, getting products to market faster, while optimizing resource utilization reduces waste and costs. The quick changeover capabilities and flexibility of CNC machines minimize downtime when switching tasks, ensuring smooth transitions between different part designs. By handling multiple operations simultaneously and adjusting cutting parameters automatically, CNC machines streamline production, reduce errors, and minimize rework. These efficiency gains result in faster delivery, higher productivity, and significant cost savings.
Repetitive Operations:: CNC machining is ideal for repetitive tasks, providing consistent quality and precise dimensions with high-speed production and long production runs. These machines work automatically, following programmed instructions to produce identical parts each time, ensuring uniform outcomes. CNC machines maintain accuracy even at high speeds, boosting productivity with faster production cycles. They excel in long runs of the same part, operating continuously without the need for frequent manual adjustments. Quality control is built into the process, with in-process inspections and post-machining measurements verifying the accuracy and quality of each part, ensuring consistency throughout repetitive operations.
Versatility:: CNC machining is a powerhouse in the manufacturing world, boasting incredible flexibility and a wide range of advantages. This technology can work with numerous materials like metals, plastics, composites, and wood, allowing manufacturers to choose the perfect material for each project. This adaptability is crucial for industries as varied as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and furniture, each with its own specific needs.
From crafting one-off prototypes to running large-scale production lines, CNC machining adapts effortlessly to any scale. It can create customized parts with precision and churn out high volumes efficiently. Moreover, CNC machines can handle additional processes such as surface treatments, heat treatment, engraving, polishing, and assembly, making them even more versatile. CNC machining’s broad capabilities and adaptability make it an indispensable tool in many industries, meeting diverse requirements with ease.
Complex Geometries:: CNC machining shines when it comes to handling intricate and complex shapes. Its prowess lies in its multi-axis capabilities and 3D cutting precision. Unlike manual machining, CNC technology can effortlessly create elaborate forms and detailed contours. Key to its success is the remarkable precision it offers, ensuring that each piece produced is a perfect replica of the original design. This accuracy is further enhanced by adaptive tooling and specialized machining strategies that tackle the challenges posed by complex features. The integration with CAD/CAM software is another pivotal aspect. Designers can craft intricate 3D models that the software translates into precise machine instructions, allowing the CNC machines to bring these designs to life with impeccable accuracy. This ability to manage complex geometries unlocks new possibilities for detailed and precise designs, especially in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical, where exacting standards are paramount.
Customization:: CNC machining stands out for its exceptional adaptability and personalization capabilities, which offer numerous significant advantages. The technology’s capacity to conform to various designs and specifications enables swift modifications and customizations. By merely updating the programming, CNC machines can seamlessly transition to producing different parts, prototypes, or adjustments as required, demonstrating a high degree of versatility in fulfilling specific demands. This adaptability is particularly advantageous in rapid prototyping and limited-run production, as it facilitates quick design iterations and customizations without the necessity for extensive retooling. Consequently, manufacturers can promptly address design alterations, market shifts, and customer preferences, ensuring a faster time-to-market and the ability to meet individual needs efficiently.
Enhanced Safety:: CNC machining significantly boosts safety, creating a secure workspace for operators. Unlike manual machining, CNC machines drastically cut down physical interaction between operators and cutting tools or workpieces, thus lowering the chances of accidents and injuries. Operators have minimal involvement in the machining process since CNC machines run independently according to programmed commands. This setup diminishes the risks of fatigue, distraction, or human mistakes leading to accidents. CNC machines come with safety measures such as emergency stop buttons, protective enclosures, and safety interlocks that restrict access to the operational area. Furthermore, advanced tool monitoring systems can identify tool wear or failures, minimizing the possibility of tool-related mishaps. By integrating safety protocols and cutting-edge technology, CNC machining ensures a safer environment, safeguarding operators and reducing potential hazards.
Lower Error Rate: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) CNC machining greatly lowers the error rate compared to manual machining, leading to better product quality. Once set up correctly, CNC machines follow the program instructions exactly, reducing mistakes that can happen with human operators due to tiredness, distraction, or inconsistency. The automation and precise control of CNC machines ensure consistent and repeatable results, minimizing deviations from the desired specifications. Furthermore, CNC machines often include built-in checks and feedback systems for real-time monitoring and adjustment during the process. This helps quickly detect and fix any errors, further reducing the error rate. By minimizing human errors and improving consistency, CNC machining delivers higher quality products and reduces the need for costly rework or scrap, boosting productivity and customer satisfaction.
Time and Cost Savings: CNC machining significantly reduces time and costs throughout the manufacturing process. Once programmed, CNC machines operate autonomously, minimizing the need for constant manual intervention and supervision. This enhances production efficiency and throughput, leading to shorter lead times and faster time-to-market. CNC machines optimize cutting parameters, reducing material waste and minimizing post-machining adjustments or rework. The precise control and automation inherent in CNC machining lower the chances of errors, avoiding time-consuming corrections. Additionally, CNC machining handles complex designs with versatile production capabilities, contributing to overall cost savings. It reduces labor costs by minimizing manual labor requirements, and the elimination of human errors and rework decreases material waste and associated costs. These time and cost savings make CNC machining a cost-effective solution for modern manufacturing operations.
CNC machining brings unmatched precision, efficiency, and adaptability to the manufacturing process, driving up productivity, quality, and cost savings. Its capacity to handle intricate designs and various materials makes it a cornerstone technology in today’s manufacturing landscape.
CNC Applications
CNC machining has countless applications, enabling manufacturers to produce parts and products for virtually all industries. In industrial manufacturing, it ensures high precision and efficiency in mass production. Many different industries rely on CNC machining for its a precision and ability to create a variety of intricate, complex, durable, precise components. From metalworking to aerospace to electronics, these industries rely on CNC production machining for high-quality, consistent results.
Manufacturers produce a variety of products to support metalworking processes, including dies, coinage dies, molds, fittings, and equipment components such as gears, shafts, and shaft assemblies. Woodworkers use CNC machining to cut, carve, and shape wooden components. This technology allows them to create intricate designs, custom furniture pieces, cabinetry, decorative moldings, and other wood products with exceptional precision and consistency.
CNC machining is essential in the automotive industry for manufacturing high-precision and reliable components such as engine parts, transmission components, chassis parts, and both interior and exterior trim pieces. In the electronics industry, CNC machining is used to produce circuit boards, connectors, heatsinks, enclosures, and other intricate parts that require precise machining to meet specific electronic device requirements. Manufacturers use CNC machining in the aerospace industry to create ground support equipment, compressor cases, control panels, separation discs, electronic enclosures, housings, and instrument panels.
CNC manufacturers produce a range of components for the energy sector, such as light assemblies, solar cells, housings, gear cases, covers, hubs, brackets, couplings, guides, sleeves, weldments, fluid manifold blocks, gas blocks, motion components, and shaft components. CNC machining is integral to furniture production, enabling precise cutting, shaping, and carving of wooden components. This technology facilitates the creation of intricate designs, custom furniture pieces, cabinetry, decorative moldings, and other wood products, leveraging its capability for complex shapes, detailed features, and efficient manufacturing. It also plays a pivotal role in the oil and gas industry, producing diverse components including spacers, connected rod bushings, pump liners, wrist pin bushings, drill bit parts, hydraulic components, electric submersible pumps, valving systems, actuating systems, sealing systems, vacuum systems, and blowout preventers.
Manufacturers utilizing CNC machines produce a wide array of products across various industries. In the marine sector, these include connecting shafts, arrester gears, valves, flanges, engine parts, propulsion systems, transmission units, power trains, and marine power units. In military and defense applications, CNC machining yields critical components such as clamshells, fuser rollers, flanges, retainer rings, track hubs, main rotor hubs, missile components, aircraft seat frames, helicopter parts, aerospace couplers, naval structural systems, shift components, engines, transmission parts, and munitions hoist components. In medicine and healthcare, CNC machined products range from spinal fusion cages, expandable rib cages, bone plates, and maxillofacial prosthetics to endovascular devices, vena cava clips, surgical forceps, equipment housings, dental scalers, and fixation devices.
Additionally, CNC technology extends into producing diverse items like household fixtures, satellite components, ball joints, valve bodies, computer assemblies, semiconductor parts, suspension arms, thermal device components, spindle housings, tensioners, fasteners, shafts, rail gears, switch gears, module blocks, and beyond.
History of CNC Machining
In the 1940s and 1950s, engineers pioneered computer numerical control (CNC) machines, early versions of motorized tools guided by punched tape inputs. Over time, analog and digital computers enhanced their capabilities. By the 1970s, manufacturers began employing basic CNC machining software practically, despite initial technological limitations. Since then, advancements in computer technology have significantly enhanced precision and reliability. Modern CNC machines feature user-friendly codes, aided by computer imaging for client-involved product design and prototype creation prior to full-scale production. Production codes are archived for future use. Today, CNC manufacturers not only produce but also offer consulting, design, and production optimization services for their clients.
CNC Machining Service Details
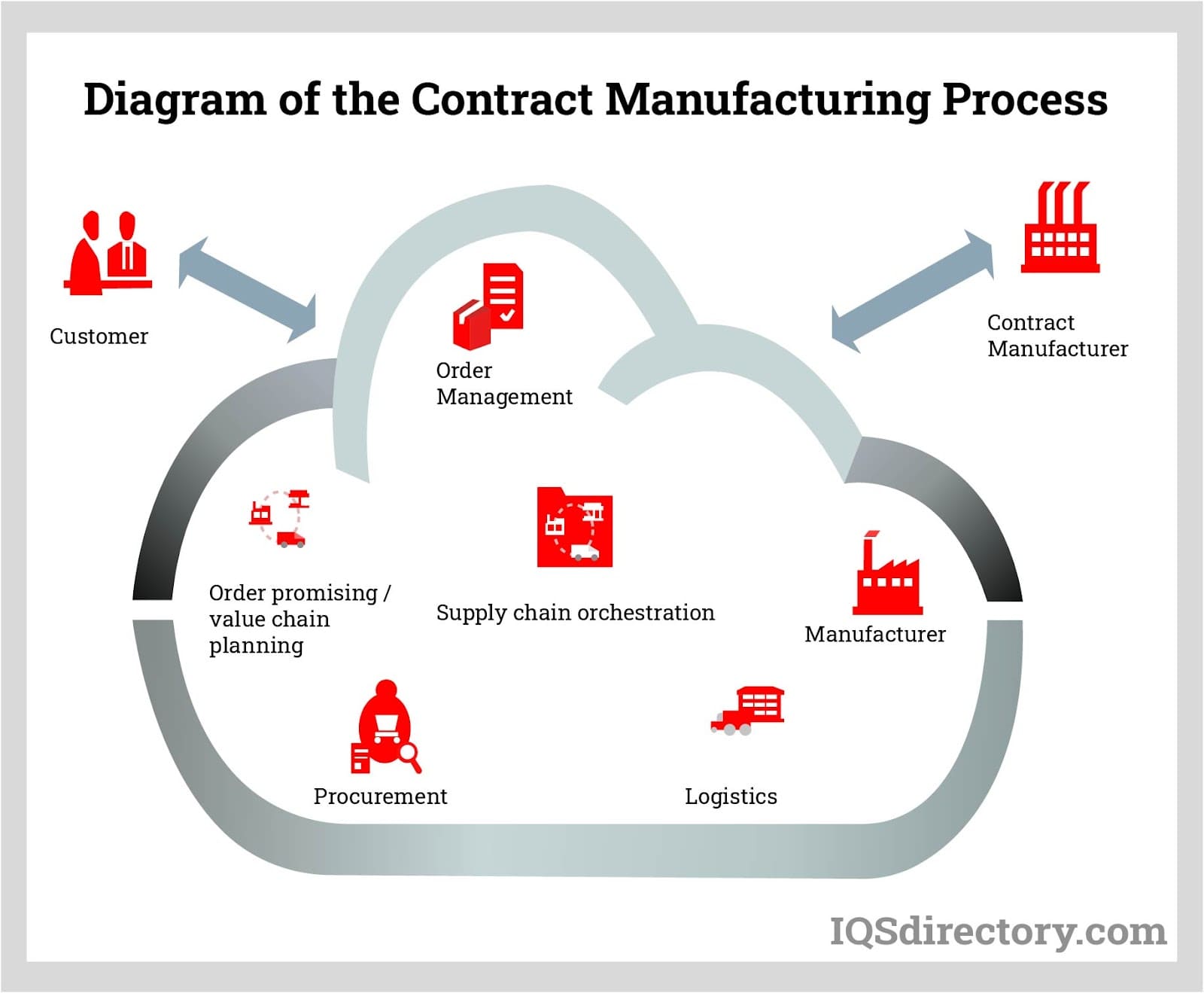
CNC machining services are professional manufacturing solutions utilizing computer-controlled machines to fabricate precise, bespoke parts according to client specifications. These services include material selection, programming, finishing, processing, and more.
CNC Manufacturers will work with a diverse array of materials such as metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, brass, titanium), plastics (e.g., ABS, PVC, nylon), composites, and wood. Material choice is tailored to meet specific application needs, desired properties, and part functionality. Clients submit design specifications, typically in 2D drawings, 3D models, or CAD files. Service providers optimize designs for manufacturability, advise on material suitability, tolerances, and machining approaches. Designs are then translated into machine-readable instructions through computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software.
The CNC machining process begins with setting up the machine, including tool installation, fixtures, and workholding devices. The pre-generated program is then uploaded into the CNC machine’s computer system. The machine executes machining operations like milling, turning, CNC drilling, and cutting according to the programmed instructions, capable of handling multi-axis operations for complex geometries and intricate details. CNC machining services incorporate stringent quality control measures to ensure parts meet required specifications. This includes in-process inspections, post-machining measurements, and the use of advanced metrology equipment such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). Inspection reports and certificates of conformance are provided to validate the quality and precision of the parts.
After CNC machining, parts may undergo additional processes tailored to client specifications. These include surface treatments such as anodizing, plating, painting, or powder coating, aimed at improving appearance, corrosion resistance, or functional properties. Additional services like deburring, polishing, and assembly may also be available. After quality checks and finishing processes, parts are meticulously packaged to ensure safe transportation. Providers offer flexible shipping options, including express and international delivery, to meet client requirements.
Effective communication and collaboration between clients and CNC machining service providers are essential throughout the machining process. Clear articulation of design specifications, material requirements, and delivery schedules is pivotal for project success. Regular updates, progress reports, and timely responses to inquiries enhance the efficiency and smoothness of service delivery.
CNC machining services offer clients advanced manufacturing capabilities, expertise in material selection and design optimization, and the convenience of outsourcing production to specialized providers. Leveraging these services enables businesses to achieve efficient production, precise parts, and accelerated turnaround times.
CNC Machinery
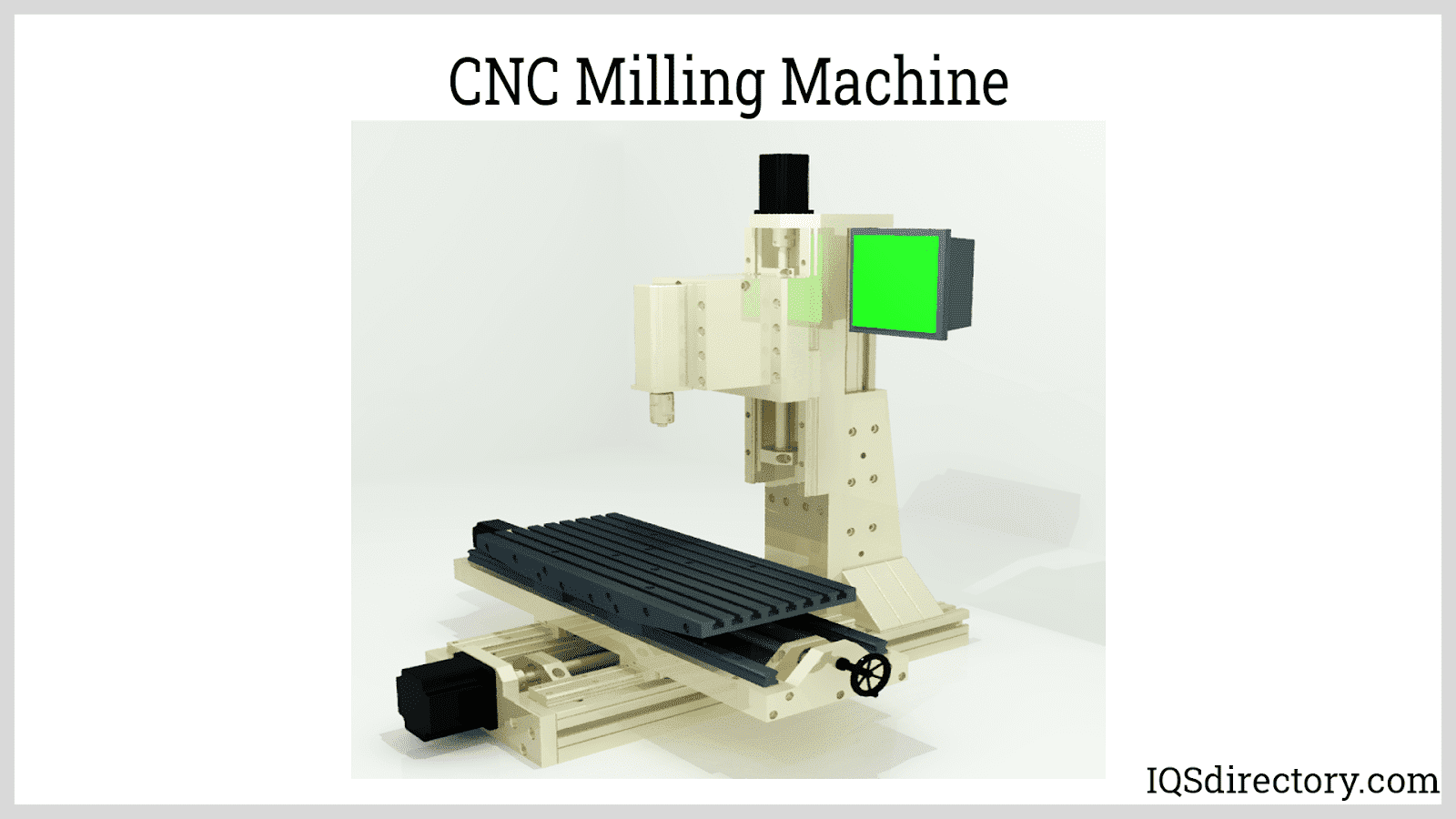
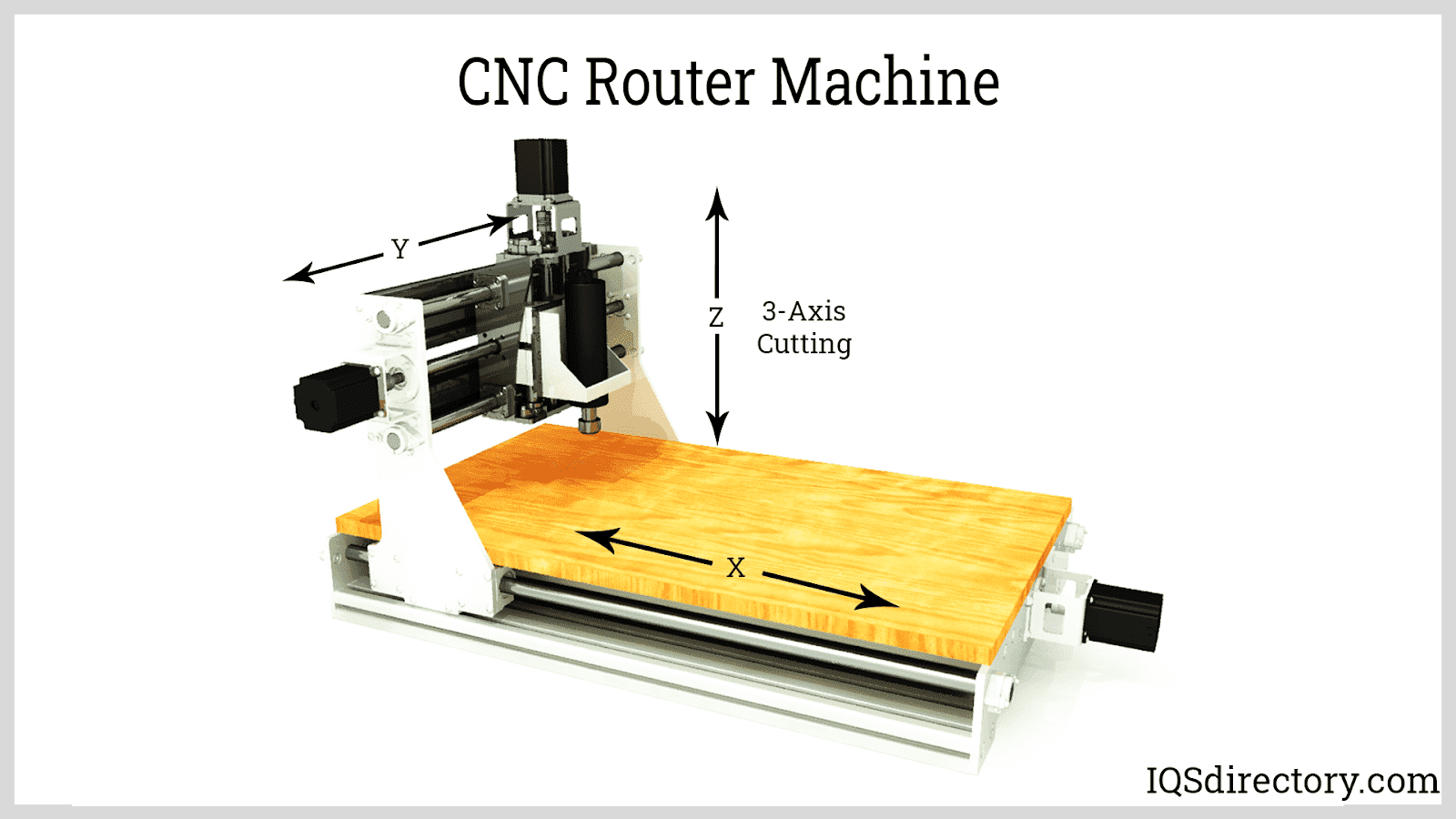
Vertical milling machines utilize cutting tools that operate along a vertical axis, enabling cutting or drilling from various angles including the front, side, or above. These machines are typically used for shaping 1D geometries. Horizontal milling machines function similarly to vertical mills but feature a rotary table, often referred to as universal tables, allowing them to work at multiple angles. While more costly than vertical mills, horizontal mills offer enhanced versatility and precision.
CNC cutting machines execute cuts with meticulous precision based on programmed instructions, operating on up to six axes simultaneously. CNC drilling machines employ multiple turrets or spindles for efficient tool changes, enabling rapid adjustments in as little as two seconds. CNC lathes, akin to turning machines, shape workpieces as they rotate, employing various tools such as drills and cutters. Modern models utilize multiple axes to handle complex projects, typically operating with G-code.
CNC Machining Variations
CNC milling, also known as CNC turning, is a prevalent method in CNC manufacturing. Precision CNC machining companies often offer specialized services in this area. CNC milling involves using rotary cutters to remove excess material from a product, making it a precision machining process ideal for engraving. This process employs various mills, such as end mills, chamfer mills, and helical mills. The term “CNC turning” refers to the machine’s rotational movement during operation. CNC milling machines excel at engraving by engaging multiple axes simultaneously with tools like cutters and conical tools, allowing manufacturers to achieve high-quality results efficiently.
Common precision CNC machining services include cutting, drilling, and grinding. These functions can be programmed into a single unit or involve several machine tool heads for specific tasks. CNC turning precisely rotates the workpiece against a single-point cutting tool. Lathes, including turret lathes and engine lathes, are the primary tools for turning operations.
CNC drilling uses computer-guided machines to bore holes of various shapes and sizes. This precision method creates cylindrical holes in materials with spinning multi-point drill bits. Versatile and efficient, CNC drilling can be used on all types of materials. Industries such as military, recreation, automotive, aerospace, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food and beverage frequently utilize this technology.
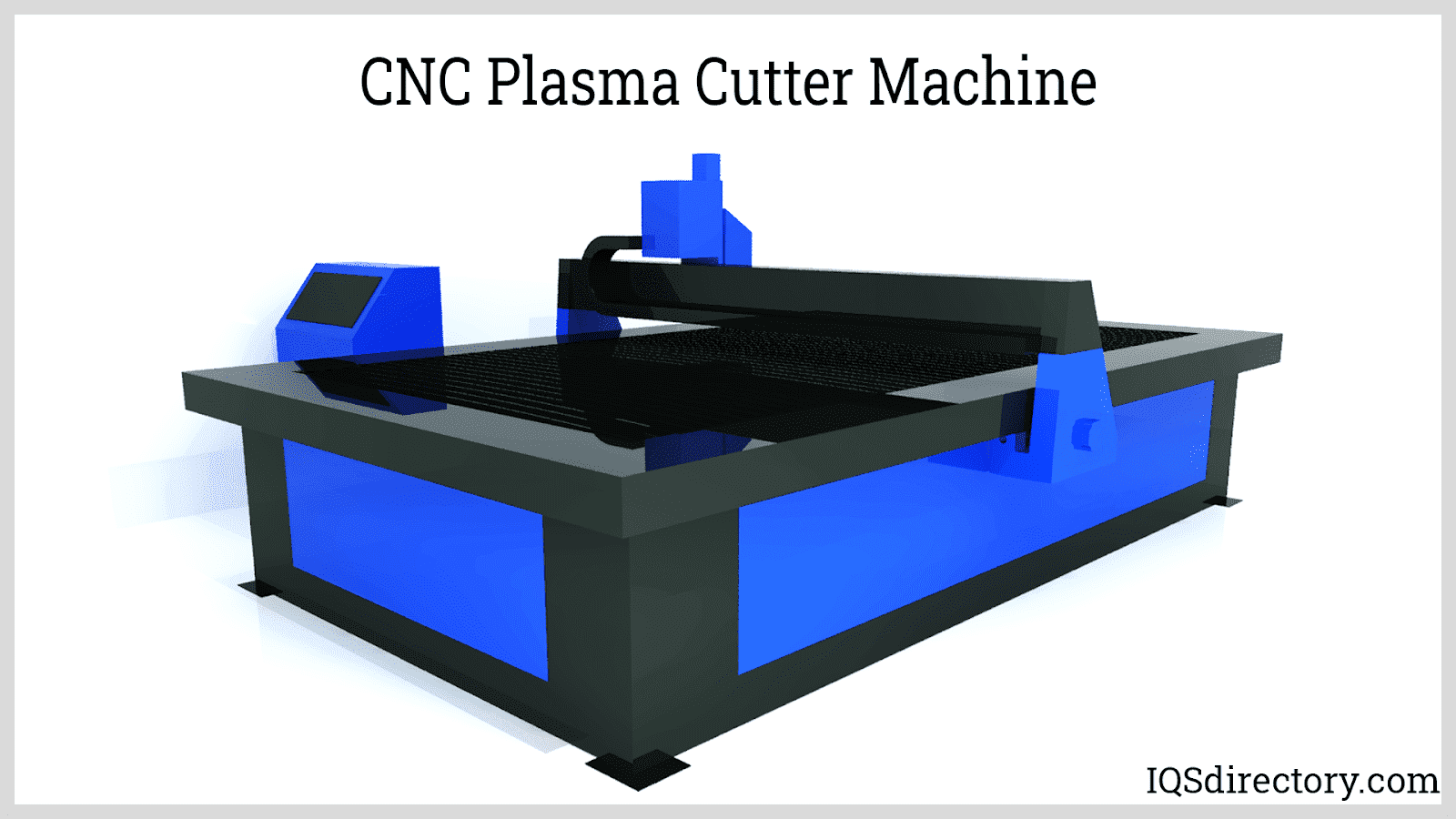
CNC grinding uses software to control an abrasive belt, disc, or wheel to finish parts by removing excess material. CNC plasma cutters employ powerful lasers to cut programmed shapes from sheets or plates. Precision CNC machining, driven by coded instructions, shapes and cuts workpieces to exact specifications without manual intervention, making it ideal for producing small parts and components used in various products.
Things to Consider Regarding CNC Machining
Manufacturers vary in their machinery capabilities; some have a limited selection, while others offer a diverse range to handle various projects. Each machining center is unique. To identify a manufacturer with the appropriate skills and capabilities for your needs, it is crucial to discuss your application requirements in detail with potential suppliers. Before engaging with candidates, compile a comprehensive list of your requirements, including request volume, standard specifications, budget, timeline, delivery preferences, and post-delivery support needs.
After compiling your list, review our recommended suppliers located midway down the page. Each supplier listed is a high-quality CNC machining provider. Compare their capabilities and services against your specifications to identify potential matches. Select three or four promising companies and contact them to discuss your application, using your specifications as a guide. Evaluate your discussions to determine the best service provider for your needs, then proceed with them.





 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals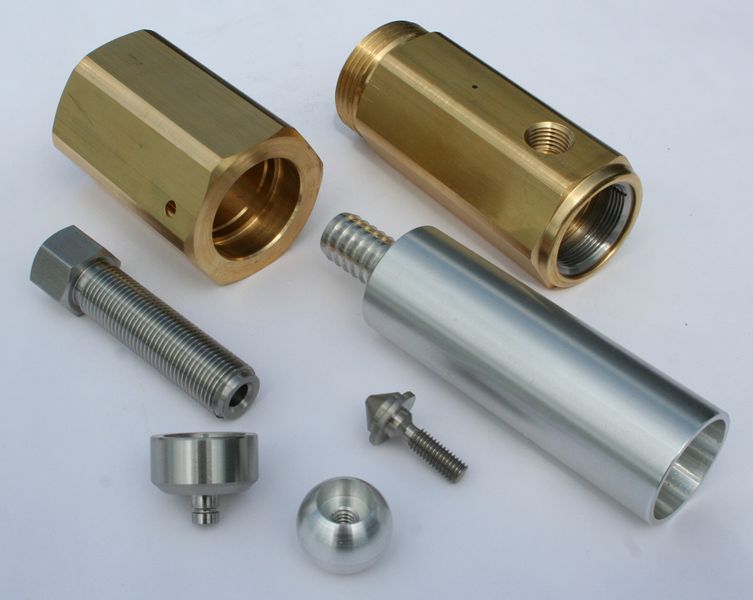 Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services